Embarking on an exploration of energy transformations, the potential versus kinetic energy worksheet serves as an interactive guide to understanding the fundamental concepts of potential and kinetic energy. Delving into the intricacies of energy conversion, this worksheet empowers learners to grasp the interplay between these two forms of energy in real-world scenarios.
By unraveling the factors influencing potential and kinetic energy, students gain insights into the mechanisms governing energy storage and motion. Through engaging activities and assessments, this worksheet fosters a comprehensive understanding of energy principles, laying the groundwork for future scientific endeavors.
Potential Energy
Potential energy is the energy stored within an object due to its position or state. It is the energy that an object has because of its position relative to a force field, such as gravity or an electric field. Examples of potential energy include the energy stored in a stretched spring, the energy stored in a raised object, and the energy stored in a charged capacitor.The
factors that affect potential energy are the mass of the object, the strength of the force field, and the distance of the object from the source of the force field. The potential energy of an object can be calculated using the following formula:“`PE = mgh“`where:* PE is the potential energy in joules (J)
- m is the mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
- g is the acceleration due to gravity in meters per second squared (m/s^2)
- h is the height of the object above the ground in meters (m)
Kinetic Energy
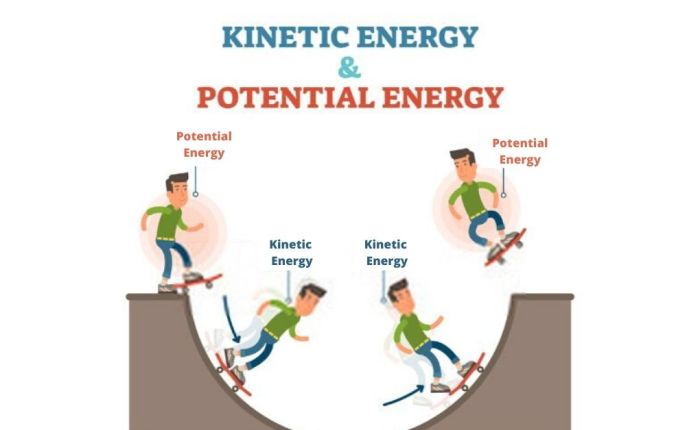
Kinetic energy is the energy of an object in motion. It is the energy that an object has because of its motion. Examples of kinetic energy include the energy of a moving car, the energy of a spinning top, and the energy of a flowing river.The
factors that affect kinetic energy are the mass of the object and the speed of the object. The kinetic energy of an object can be calculated using the following formula:“`KE = 1/2 mv^2“`where:* KE is the kinetic energy in joules (J)
- m is the mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
- v is the speed of the object in meters per second (m/s)
Conversion of Energy
Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy, and kinetic energy can be converted into potential energy. For example, when a ball is dropped, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy as it falls. When the ball hits the ground, its kinetic energy is converted into potential energy as it rebounds.There
are many examples of energy conversion in everyday life. For example, when you turn on a light, the electrical energy from the battery or power outlet is converted into light energy. When you ride a bike, the chemical energy in your food is converted into kinetic energy as you pedal.
Applications of Potential and Kinetic Energy

Potential energy and kinetic energy are used in many applications in everyday life. For example, potential energy is used in roller coasters, bows and arrows, and hydroelectric dams. Kinetic energy is used in cars, airplanes, and wind turbines.Here are some examples of devices that use potential and kinetic energy:*
-*Roller coasters
Roller coasters use potential energy at the top of the hill and kinetic energy at the bottom of the hill.
-
-*Bows and arrows
Bows and arrows use potential energy when the bow is drawn and kinetic energy when the arrow is released.
-*Hydroelectric dams
Hydroelectric dams use potential energy from the water behind the dam to generate electricity.
-*Cars
Cars use kinetic energy to move and potential energy when they are parked on a hill.
-*Airplanes
Airplanes use kinetic energy to fly and potential energy when they are climbing.
-*Wind turbines
Wind turbines use kinetic energy from the wind to generate electricity.
FAQ Overview: Potential Versus Kinetic Energy Worksheet
What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is stored energy due to an object’s position or condition, while kinetic energy is energy of motion.
How can potential energy be converted into kinetic energy?
Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy through movement, such as when an object falls or rolls.
What are some examples of devices that use potential and kinetic energy?
Examples include roller coasters, pendulums, and hydroelectric dams.