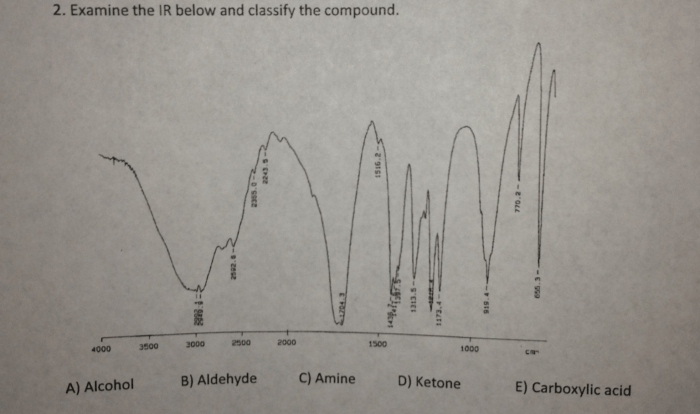
What products are expected in the ethoxide-promoted – In the realm of organic synthesis, the ethoxide-promoted reaction stands out as a powerful tool for crafting a diverse array of compounds. This reaction, characterized by its unique mechanisms and versatile applications, offers a glimpse into the intricate world of chemical transformations.
Delve into this comprehensive exploration to unravel the expected products of ethoxide-promoted reactions, unlocking their potential for innovation and discovery.
Product Characteristics
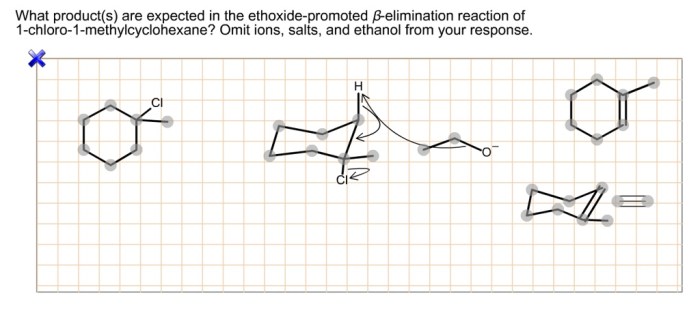
The ethoxide-promoted reaction typically yields a variety of products, depending on the starting materials and reaction conditions. The expected products include:
- Esters: Esters are formed by the reaction of an acid chloride with an alcohol in the presence of ethoxide ion. Esters are characterized by their carbonyl group (-C=O) and alkoxy group (-OR).
- Ethers: Ethers are formed by the reaction of an alkyl halide with an alcohol in the presence of ethoxide ion. Ethers are characterized by their two alkyl or aryl groups (-R) bonded to an oxygen atom (-O-).
- Ketones: Ketones are formed by the reaction of an acid chloride with a ketone in the presence of ethoxide ion. Ketones are characterized by their carbonyl group (-C=O) and two alkyl or aryl groups (-R).
- Aldehydes: Aldehydes are formed by the reaction of an acid chloride with an aldehyde in the presence of ethoxide ion. Aldehydes are characterized by their carbonyl group (-C=O) and one alkyl or aryl group (-R).
Reaction Mechanisms
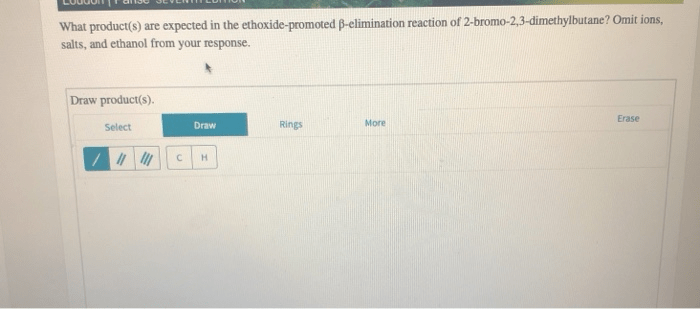
The ethoxide-promoted reaction proceeds through a nucleophilic substitution mechanism. The ethoxide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom of the acid chloride, alkyl halide, or ketone. This results in the formation of a new bond between the ethoxide ion and the carbon atom, and the departure of the leaving group (chloride ion, bromide ion, or water).
The reaction can proceed through either an SN2 or SN1 mechanism, depending on the nature of the starting materials and the reaction conditions. In an SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon atom in a concerted manner, resulting in the inversion of configuration at the carbon atom.
In an SN1 reaction, the leaving group first departs from the electrophilic carbon atom, forming a carbocation, which is then attacked by the nucleophile.
Reaction Conditions
The ethoxide-promoted reaction is typically carried out in a polar aprotic solvent, such as dimethylformamide (DMF) or dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). The reaction temperature can vary depending on the starting materials and the desired products. The reaction is typically complete within a few hours to a few days.
The yield and selectivity of the reaction can be affected by a number of factors, including the nature of the starting materials, the reaction temperature, and the solvent. The use of a strong base, such as sodium ethoxide, can help to increase the yield of the reaction.
Applications: What Products Are Expected In The Ethoxide-promoted

The ethoxide-promoted reaction is a versatile synthetic method that can be used to prepare a variety of organic compounds. The reaction is particularly useful for the synthesis of esters, ethers, ketones, and aldehydes.
The ethoxide-promoted reaction has been used in the synthesis of a number of natural products, pharmaceuticals, and other valuable compounds. For example, the reaction has been used to synthesize the antibiotic erythromycin and the anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen.
Query Resolution
What are the key characteristics of the expected products in ethoxide-promoted reactions?
The expected products in ethoxide-promoted reactions typically possess specific functional groups, such as ethers, alcohols, or carbonyl compounds. They exhibit distinct molecular properties, including polarity, solubility, and reactivity, which influence their behavior in subsequent reactions and applications.
How does the ethoxide ion influence the reaction mechanisms in ethoxide-promoted reactions?
The ethoxide ion acts as a nucleophile, attacking electrophilic centers in the substrate. Its basicity also enables deprotonation reactions, leading to the formation of enolate intermediates. These mechanisms dictate the regio- and stereoselectivity of the reaction, ultimately determining the structure of the expected products.
What are the optimal reaction conditions for ethoxide-promoted reactions?
Ethoxide-promoted reactions typically proceed under mild conditions, often at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures. The choice of solvent and base can significantly impact the reaction rate, yield, and product distribution. Optimization of these parameters is crucial for achieving the desired outcomes.