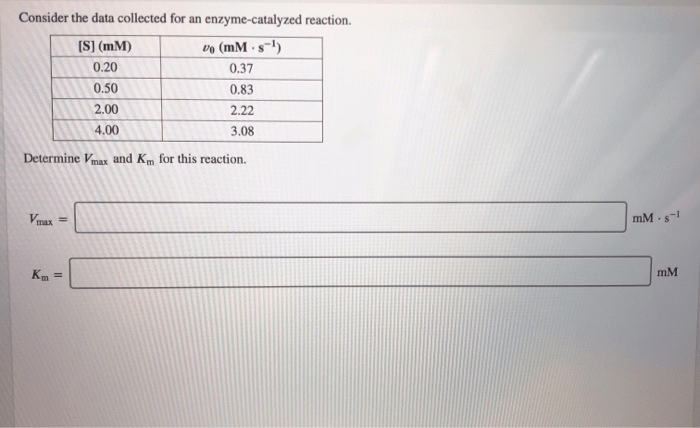
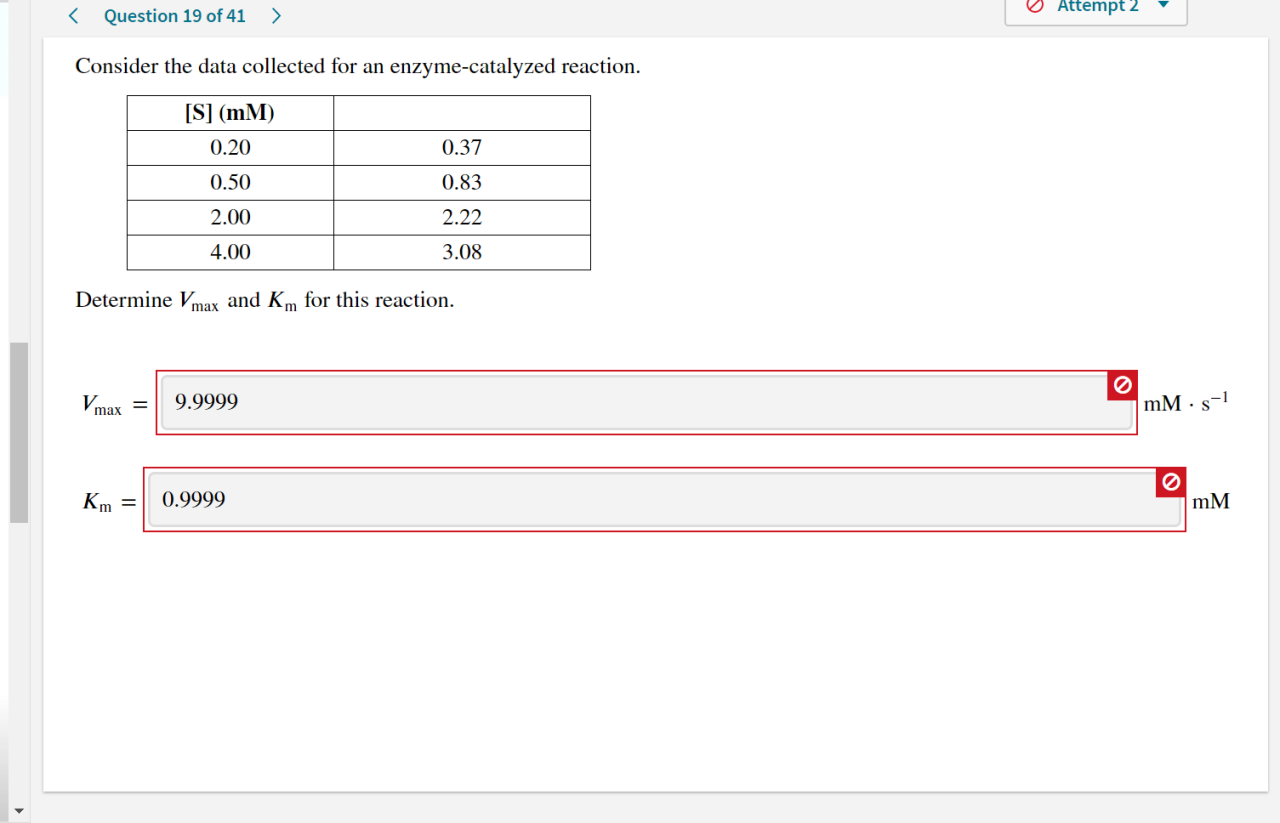
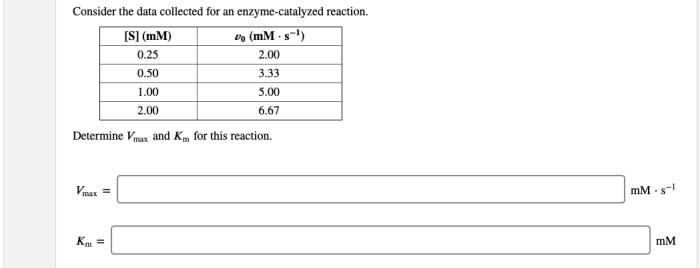
Consider the data collected for an enzyme catalyzed reaction – Consider the data collected for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction and delve into a captivating exploration of the intricate relationship between enzymes and their remarkable ability to facilitate biochemical transformations. This journey will uncover the types of data collected, the techniques employed for data acquisition, and the significance of accurate and reliable data in unraveling the mysteries of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
The analysis of enzyme-catalyzed reaction data unveils a treasure trove of insights, empowering researchers to decipher the mechanisms underlying enzyme function. Discover the diverse methods used for data analysis, their advantages and limitations, and how they have illuminated our understanding of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
Moreover, this exploration will delve into the challenges of data interpretation, highlighting strategies for identifying and mitigating potential sources of error, ensuring the validity of conclusions drawn from enzyme-catalyzed reaction data.
Enzyme-Catalyzed Reaction Data: Consider The Data Collected For An Enzyme Catalyzed Reaction
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions are fundamental to life, and understanding their behavior is essential for advancing our knowledge of biology and developing new therapies. To study these reactions, researchers collect a variety of data, including:
- Reaction rates
- Substrate concentrations
- Product concentrations
- Enzyme concentrations
- Temperature
- pH
These data are collected using a variety of experimental techniques, including:
- Spectrophotometry
- Fluorimetry
- Chromatography
- Mass spectrometry
It is important to collect accurate and reliable data in order to obtain meaningful results. This can be challenging, as enzyme-catalyzed reactions are often complex and can be influenced by a variety of factors.
Data Analysis Methods
Once data has been collected, it must be analyzed in order to extract meaningful information. There are a variety of methods available for analyzing enzyme-catalyzed reaction data, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Graphical analysis: This method involves plotting the data on a graph and visually examining the relationship between the variables.
- Statistical analysis: This method involves using statistical techniques to analyze the data and determine the significance of the results.
- Mathematical modeling: This method involves developing mathematical models to describe the behavior of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
The choice of data analysis method depends on the specific question being asked and the type of data that has been collected.
Data Interpretation
Once the data has been analyzed, it must be interpreted in order to draw conclusions about the enzyme-catalyzed reaction. This can be challenging, as there are often multiple factors that can influence the results.
It is important to identify and control for potential sources of error when interpreting the data. These sources of error can include:
- Experimental error
- Measurement error
- Data analysis error
By carefully considering the potential sources of error, researchers can increase the confidence in their conclusions.
Applications of Data Analysis

Data analysis has been used to advance our understanding of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a variety of ways. For example, data analysis has been used to:
- Determine the kinetic parameters of enzyme-catalyzed reactions
- Identify the rate-limiting step in enzyme-catalyzed reactions
- Develop new inhibitors and activators of enzyme-catalyzed reactions
Data analysis is also essential for the design and optimization of enzyme-catalyzed reactions for use in biotechnology and medicine.
FAQ
What types of data are collected for enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
Data collected includes reaction rates, substrate concentrations, product concentrations, enzyme concentrations, and pH.
How is data analysis used to study enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
Data analysis is used to determine enzyme kinetic parameters, such as Michaelis constant (Km) and maximum velocity (Vmax), and to investigate enzyme mechanisms.
What are the challenges of interpreting enzyme-catalyzed reaction data?
Challenges include identifying and controlling for potential sources of error, such as enzyme impurities, substrate purity, and temperature variations.