Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. central canal – Delving into the intricacies of the central canal, this comprehensive guide unravels its anatomical location, embryological development, and functional significance in cerebrospinal fluid circulation and blood-brain barrier formation.
Exploring its clinical implications, we delve into central canal stenosis and enlargement, their impact on cerebrospinal fluid flow and neurological function, and the diagnostic techniques employed to visualize the canal using MRI and CT.
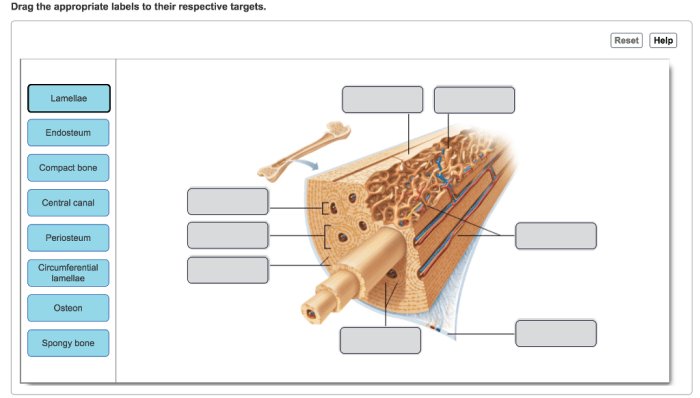
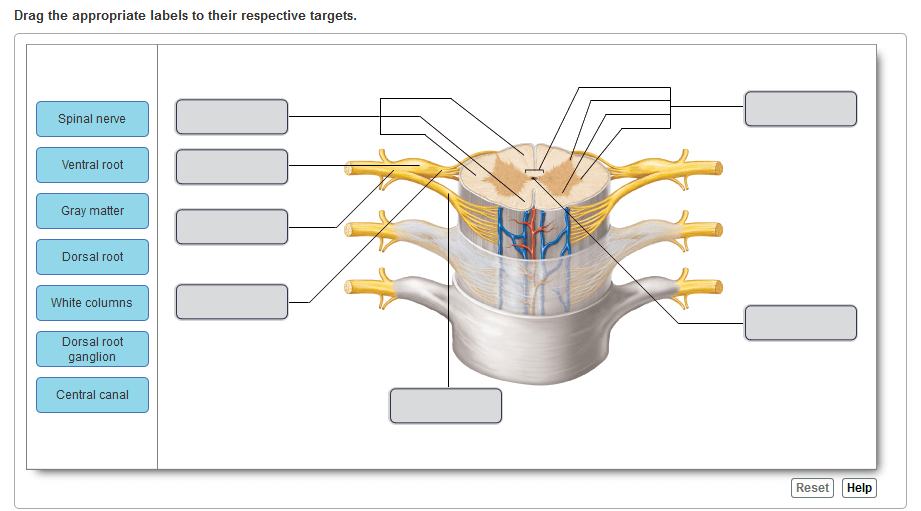
Central Canal
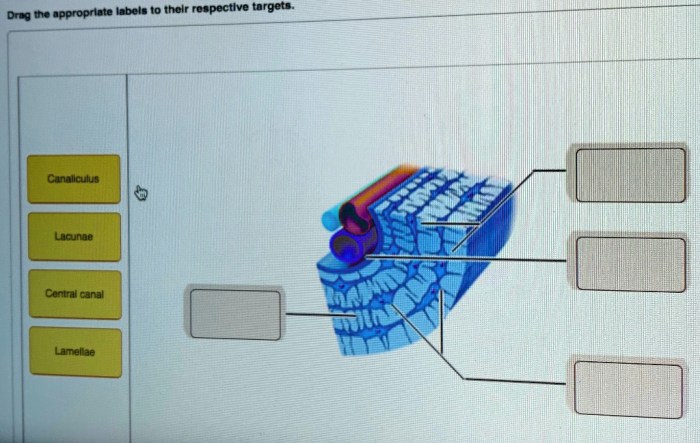
The central canal is a fluid-filled channel that runs longitudinally through the spinal cord. It is lined by ependymal cells and is continuous with the ventricles of the brain. The central canal plays a role in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and the formation of the blood-brain barrier.
Embryological Development
The central canal is formed during the development of the neural tube. The neural tube is a structure that gives rise to the brain and spinal cord. As the neural tube closes, a lumen forms within it. This lumen becomes the central canal.
Functions
The central canal has several important functions, including:
- Circulation of CSF: The central canal is part of the CSF circulatory system. CSF is a clear fluid that bathes the brain and spinal cord. It provides nutrients and oxygen to these tissues and removes waste products.
- Formation of the blood-brain barrier: The blood-brain barrier is a semipermeable membrane that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It helps to protect these tissues from harmful substances in the blood.
Pathophysiology
Central canal stenosis or enlargement can lead to a variety of clinical problems, including:
- Syringomyelia: Syringomyelia is a condition in which a cyst forms within the central canal. This cyst can compress the spinal cord and cause neurological problems, such as weakness, numbness, and pain.
- Hydromyelia: Hydromyelia is a condition in which the central canal is enlarged. This can also lead to neurological problems, such as weakness, numbness, and pain.
Diagnostic Imaging
The central canal can be visualized on imaging studies, such as MRI and CT. These studies can help to diagnose central canal stenosis or enlargement.
Treatment Options, Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. central canal
The treatment for central canal disorders depends on the severity of the condition. In some cases, no treatment is necessary. In other cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a cyst or to enlarge the central canal.
Future Directions in Research
There are several emerging research areas related to the central canal. These areas include:
- The role of the central canal in the development of syringomyelia and hydromyelia.
- The use of stem cells to treat central canal disorders.
- The development of new imaging techniques to visualize the central canal.
Question & Answer Hub: Drag The Appropriate Labels To Their Respective Targets. Central Canal
What is the central canal?
The central canal is a fluid-filled cavity located at the center of the spinal cord, extending from the brainstem to the lower end of the spinal cord.
What is the function of the central canal?
The central canal plays a crucial role in cerebrospinal fluid circulation, facilitating the flow of cerebrospinal fluid throughout the central nervous system.
What are the clinical implications of central canal abnormalities?
Central canal stenosis (narrowing) and enlargement can disrupt cerebrospinal fluid flow, potentially leading to neurological symptoms such as weakness, numbness, and impaired balance.