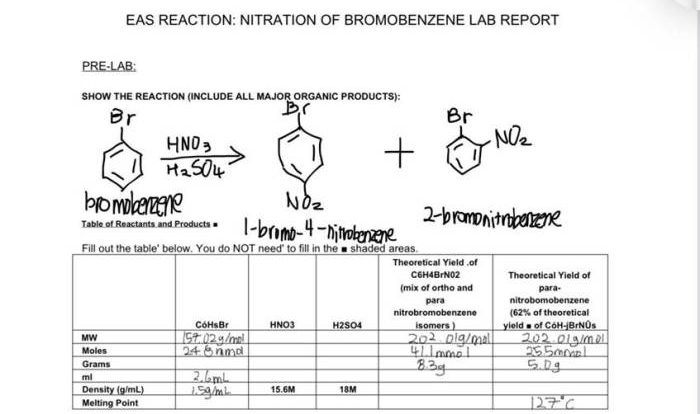
Examine the IR below and classify the compound. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique that allows chemists to identify and characterize organic compounds. By analyzing the IR spectrum of a compound, we can determine the functional groups present and use this information to classify the compound.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the IR spectrum, explaining the different regions and their corresponding functional groups. We will then demonstrate how to use this information to classify a compound and identify its structural features.
The IR spectrum is a plot of the absorbance of infrared radiation by a compound as a function of the wavenumber. The wavenumber is expressed in units of cm-1 and is inversely proportional to the wavelength of the radiation. The IR spectrum is divided into several regions, each of which corresponds to a particular type of functional group.
The most important regions are the fingerprint region (4000-1500 cm-1), the functional group region (1500-600 cm-1), and the overtone region (2000-2500 cm-1).
Examine the IR Below
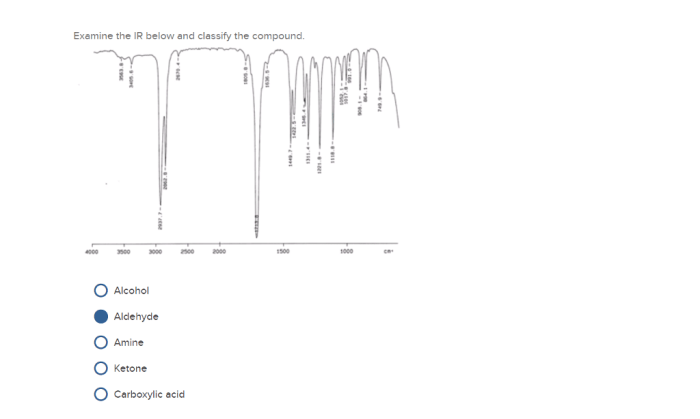
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to identify functional groups present in a molecule. The IR spectrum is a plot of the absorbance of infrared radiation by a sample as a function of the frequency of the radiation.
Different functional groups absorb infrared radiation at characteristic frequencies, which allows them to be identified.
The IR spectrum is divided into several regions, each of which corresponds to a different type of functional group. The most important regions are:
- The fingerprint region (1200-800 cm-1): This region is used to identify specific functional groups. Each functional group has a unique set of absorption bands in this region, which allows it to be easily identified.
- The functional group region (1800-1200 cm-1): This region is used to identify the major functional groups present in a molecule. The most common functional groups that absorb in this region are C=O, C-O, and N-H.
- The overtone region (2800-2000 cm-1): This region is used to identify overtones and combination bands. Overtones are harmonics of the fundamental vibrations, while combination bands are the result of two or more fundamental vibrations occurring simultaneously.
By carefully examining the IR spectrum of a compound, it is possible to identify the functional groups present and determine the structure of the molecule.
Classify the Compound
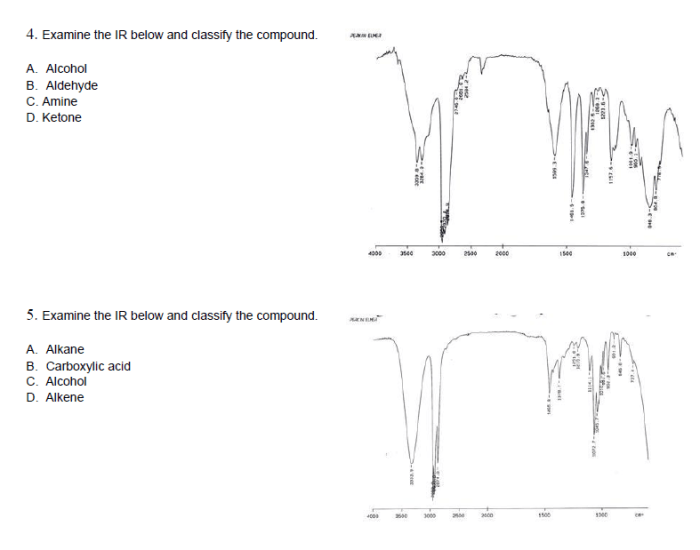
Once the functional groups present in a compound have been identified, it is possible to classify the compound into a specific group. The most common classes of compounds are:
- Alkanes:Alkanes are hydrocarbons that contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms. They have a general formula of C nH 2n+2.
- Alkenes:Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. They have a general formula of C nH 2n.
- Alkynes:Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. They have a general formula of C nH 2n-2.
- Alcohols:Alcohols are organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl group (-OH). They have a general formula of R-OH.
- Ethers:Ethers are organic compounds that contain an ether group (-O-). They have a general formula of R-O-R’.
- Aldehydes:Aldehydes are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (-CHO). They have a general formula of R-CHO.
- Ketones:Ketones are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (-CO-). They have a general formula of R-CO-R’.
- Carboxylic acids:Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH). They have a general formula of R-COOH.
By classifying a compound into a specific group, it is possible to predict its properties and reactivity.
Identify Structural Features
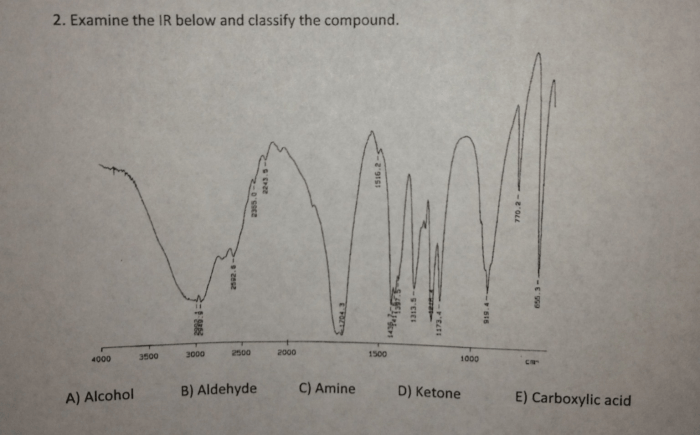
The IR spectrum of a compound can also be used to identify specific structural features. For example, the presence of a strong absorption band at 1710 cm -1indicates the presence of a carbonyl group. The presence of a broad absorption band between 3200 and 3600 cm -1indicates the presence of a hydroxyl group.
The presence of a sharp absorption band at 2250 cm -1indicates the presence of a nitrile group.
By carefully examining the IR spectrum of a compound, it is possible to identify a variety of structural features, including:
- The presence of specific functional groups
- The presence of specific structural features, such as rings or double bonds
- The stereochemistry of the molecule
The IR spectrum is a powerful tool for identifying the structure of a compound.
Compare and Contrast
The IR spectrum of an unknown compound can be compared to the IR spectra of known compounds in order to identify the unknown compound or to identify potential impurities. By comparing the IR spectra of two compounds, it is possible to identify similarities and differences between the two compounds.
For example, if the IR spectrum of an unknown compound is similar to the IR spectrum of a known alkane, then it is likely that the unknown compound is also an alkane. If the IR spectrum of an unknown compound is different from the IR spectrum of a known alkane, then it is likely that the unknown compound is not an alkane.
By comparing the IR spectra of two compounds, it is possible to gain valuable information about the structure and identity of the unknown compound.
Create a Table: Examine The Ir Below And Classify The Compound.
The following table summarizes the functional groups that can be identified using IR spectroscopy, along with their corresponding wavenumbers and intensities.
| Functional Group | Wavenumber (cm-1) | Intensity |
|---|---|---|
| C-H stretch | 2850-3000 | Strong |
| O-H stretch | 3200-3600 | Broad |
| N-H stretch | 3300-3500 | Medium |
| C=O stretch | 1710-1750 | Strong |
| C-O stretch | 1000-1300 | Medium |
| C-N stretch | 1250-1350 | Medium |
Helpful Answers
What is the IR spectrum?
The IR spectrum is a plot of the absorbance of infrared radiation by a compound as a function of the wavenumber.
What are the different regions of the IR spectrum?
The most important regions are the fingerprint region (4000-1500 cm-1), the functional group region (1500-600 cm-1), and the overtone region (2000-2500 cm-1).
How can I use the IR spectrum to classify a compound?
By identifying the key functional groups present in the IR spectrum, we can use this information to classify the compound.