Ap macro topic 5.2 the phillips curve worksheet answers – The Phillips Curve, a cornerstone of macroeconomic analysis, has played a pivotal role in shaping economic policy. This worksheet delves into the intricacies of the Phillips Curve, exploring its historical context, limitations, extensions, and relevance in the modern economy. Engage in this exploration and deepen your understanding of this fundamental economic concept.
The Phillips Curve: Ap Macro Topic 5.2 The Phillips Curve Worksheet Answers
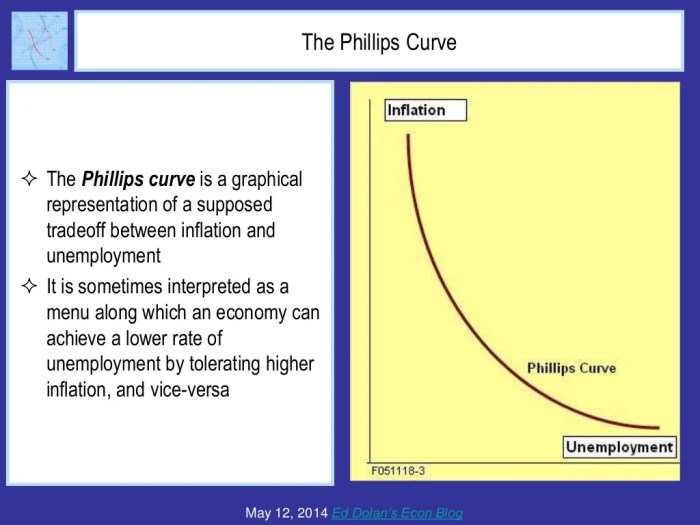
The Phillips curve is a graphical representation of the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. It was first proposed by economist A.W. Phillips in 1958 and has since become a widely used tool for analyzing economic policy.
Relationship between Inflation and Unemployment
The Phillips curve suggests that there is a trade-off between inflation and unemployment. When inflation is high, unemployment tends to be low, and vice versa. This is because when the economy is growing and inflation is rising, businesses are more likely to hire workers and expand their operations.
As a result, unemployment falls.
Conversely, when inflation is low, businesses are less likely to hire workers and may even lay off employees. This is because when inflation is low, consumers are less likely to spend money, and businesses are less likely to invest. As a result, unemployment rises.
Real-World Examples
The Phillips curve has been used to guide economic policy in many countries around the world. For example, in the United States, the Federal Reserve often uses the Phillips curve to set interest rates. When inflation is high, the Fed will raise interest rates to slow down the economy and reduce inflation.
When unemployment is high, the Fed will lower interest rates to stimulate the economy and create jobs.
Limitations of the Phillips Curve
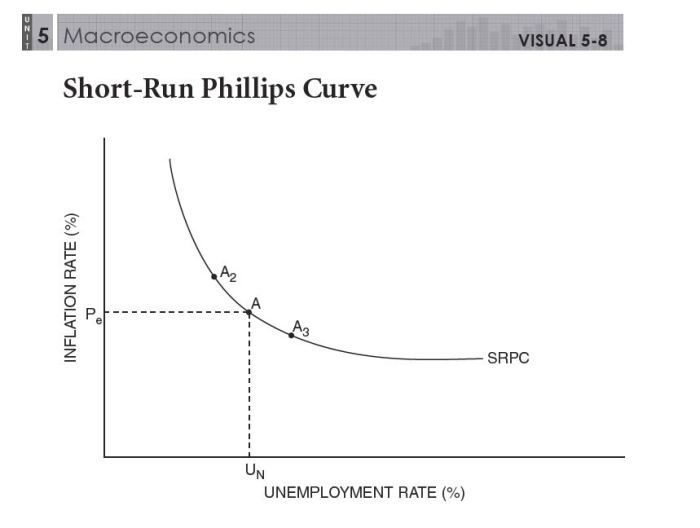
Shifts in the Phillips Curve
The Phillips curve is not a static relationship. It can shift over time due to a number of factors, including:
- Changes in technology
- Changes in government policy
- Changes in consumer expectations
For example, if there is a technological breakthrough that makes it easier for businesses to produce goods and services, the Phillips curve will shift to the right. This is because businesses will be able to produce more goods and services with the same number of workers, which will reduce unemployment.
However, it will also put downward pressure on prices, which will reduce inflation.
Natural Rate of Unemployment
The natural rate of unemployment is the level of unemployment that exists in an economy when there is no inflation. This is because at the natural rate of unemployment, the number of people who are looking for jobs is equal to the number of jobs that are available.
As a result, there is no upward or downward pressure on wages, and inflation remains stable.
The natural rate of unemployment is not a fixed number. It can vary depending on a number of factors, including the structure of the economy, the level of education and skills of the workforce, and the rate of technological change.
Criticisms and Limitations, Ap macro topic 5.2 the phillips curve worksheet answers
The Phillips curve has been criticized for a number of reasons, including:
- It is not always accurate. In some cases, inflation and unemployment have moved in the same direction.
- It is not a causal relationship. The Phillips curve does not show that inflation causes unemployment or vice versa. It simply shows that there is a correlation between the two.
- It is not a reliable guide for economic policy. The Phillips curve can shift over time, which makes it difficult to use it to predict the future.
Extensions of the Phillips Curve
Expectations-Augmented Phillips Curve
The expectations-augmented Phillips curve is a modification of the traditional Phillips curve that takes into account the role of expectations in shaping the relationship between inflation and unemployment. The expectations-augmented Phillips curve suggests that inflation is determined by both the current level of unemployment and the expected future level of inflation.
This is because when workers and businesses expect inflation to be high in the future, they will demand higher wages and prices today. This will lead to higher inflation today, which will then lead to higher inflation in the future.
As a result, the expectations-augmented Phillips curve is steeper than the traditional Phillips curve.
Role of Expectations
Expectations play an important role in the relationship between inflation and unemployment. If workers and businesses expect inflation to be high in the future, they will demand higher wages and prices today. This will lead to higher inflation today, which will then lead to higher inflation in the future.
As a result, the expectations-augmented Phillips curve is steeper than the traditional Phillips curve.
Conversely, if workers and businesses expect inflation to be low in the future, they will demand lower wages and prices today. This will lead to lower inflation today, which will then lead to lower inflation in the future. As a result, the expectations-augmented Phillips curve is flatter than the traditional Phillips curve.
Examples
The expectations-augmented Phillips curve has been used to explain a number of economic phenomena, including:
- The high inflation of the 1970s
- The low inflation of the 1990s and 2000s
- The recent rise in inflation
The Phillips Curve in the 21st Century
Challenges to the Traditional Phillips Curve
The traditional Phillips curve has been challenged in recent decades by a number of factors, including:
- Globalization
- Technological change
- The rise of the service sector
These factors have made it more difficult to use the Phillips curve to predict the future of inflation and unemployment.
Secular Stagnation
Secular stagnation is a term used to describe a period of slow economic growth and low inflation. This is a challenge to the traditional Phillips curve, which suggests that there is a trade-off between inflation and unemployment. In a period of secular stagnation, there is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
Instead, both inflation and unemployment can be low.
Alternative Models
A number of alternative models have been proposed to explain the relationship between inflation and unemployment in the modern economy. These models include:
- The New Keynesian Phillips curve
- The hysteresis model
- The structural unemployment model
These models provide different explanations for the relationship between inflation and unemployment, and they can be used to make different predictions about the future of the economy.
FAQ Explained
What is the Phillips Curve?
The Phillips Curve depicts the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment, suggesting that higher inflation is associated with lower unemployment, and vice versa.
What are the limitations of the Phillips Curve?
The Phillips Curve can shift due to factors such as technological advancements, globalization, and changes in expectations, limiting its predictive power.
What is the “natural rate of unemployment”?
The natural rate of unemployment represents the lowest level of unemployment achievable without triggering inflationary pressures.