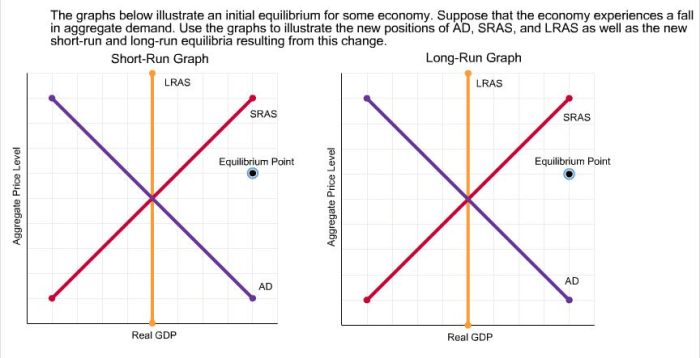
The graphs illustrate an initial equilibrium for some economy, providing a foundation for understanding the intricate interplay of supply and demand. This analysis unveils the factors that shape economic outcomes, revealing the dynamic nature of markets and their responsiveness to external influences.
Initial equilibrium represents a state of balance where supply and demand converge at a specific price and quantity, establishing a stable market condition. This concept forms the cornerstone of economic analysis, enabling policymakers and economists to assess market dynamics and predict future trends.
Overview of Initial Equilibrium
Initial equilibrium in economics represents a state of balance in a market where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at a specific price. This equilibrium point establishes a stable market condition where there is no tendency for prices or quantities to change.
Graphical Representation of Initial Equilibrium: The Graphs Illustrate An Initial Equilibrium For Some Economy
| Supply | Demand | Equilibrium Price | Equilibrium Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
P* | Q* |
The graph depicts the initial equilibrium point (P*, Q*) where the supply and demand curves intersect.
Analysis of Supply and Demand Curves
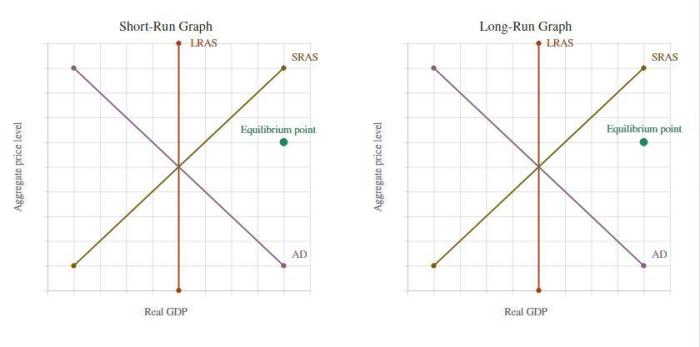
The supply curve represents the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that producers are willing and able to supply. The demand curve represents the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that consumers are willing and able to demand.
Shifts in the supply or demand curves can lead to changes in the equilibrium point. For example, an increase in demand, represented by a rightward shift of the demand curve, will lead to a higher equilibrium price and quantity.
Market Dynamics and Equilibrium
Market forces, such as changes in consumer preferences or technological advancements, can influence the equilibrium point. Government interventions, such as price controls, can also affect the equilibrium point.
Deviations from the initial equilibrium point can occur due to factors such as supply shocks or changes in consumer behavior.
Applications of Initial Equilibrium Analysis
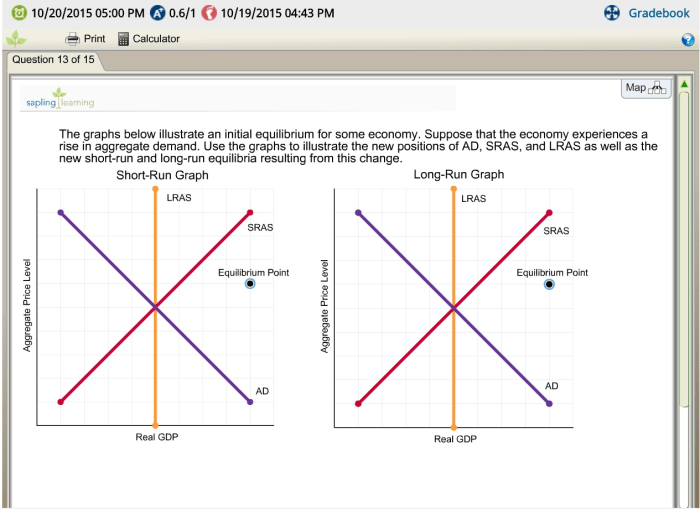
Initial equilibrium analysis is used in economic policymaking to understand the impact of government policies on market outcomes.
Limitations of initial equilibrium analysis include its static nature and its assumption of perfect competition. However, it provides a useful framework for understanding the fundamental forces that determine market outcomes.
Quick FAQs
What is initial equilibrium in economics?
Initial equilibrium occurs when supply and demand intersect at a specific price and quantity, establishing a stable market condition.
How do supply and demand curves determine equilibrium?
The intersection of the supply and demand curves establishes the equilibrium point, where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded.
What factors can shift supply and demand curves?
Factors such as technological advancements, changes in consumer preferences, and government policies can shift supply and demand curves, leading to new equilibrium points.